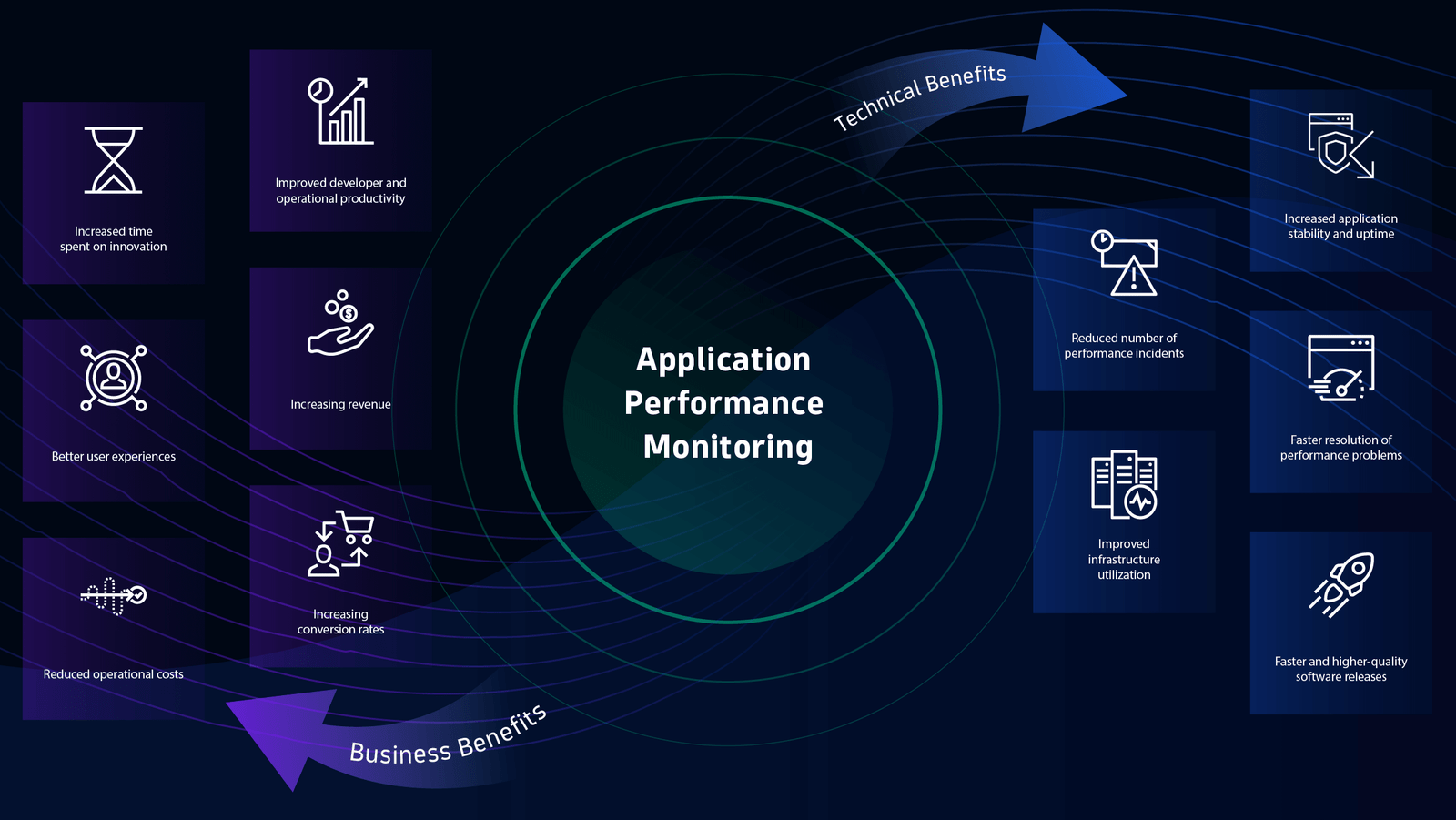
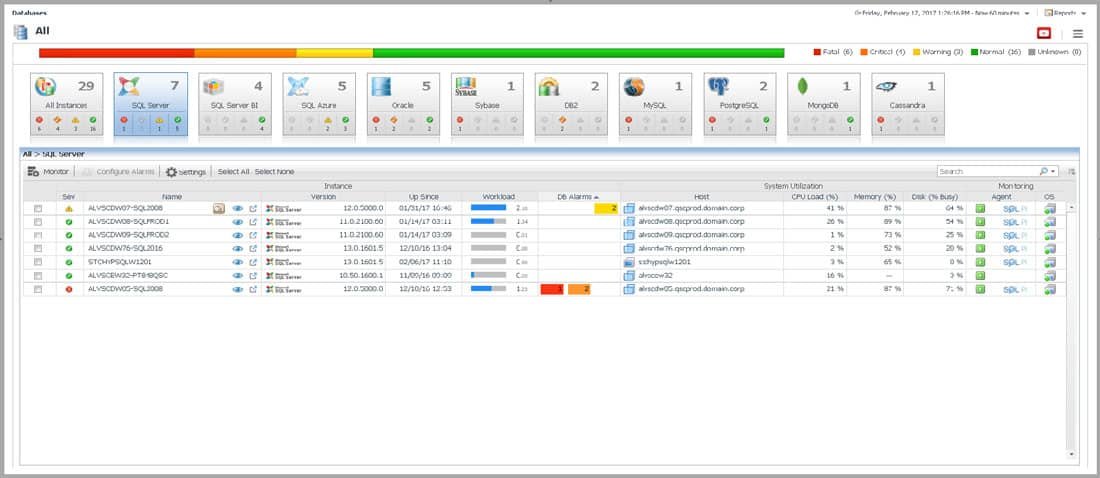
Developing an operating system (OS) is a complex task that requires a deep understanding of hardware and software interactions. To facilitate this process, developers rely on various Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and Software Development Kits (SDKs). These tools provide essential functionality, streamline development, and help manage the intricacies of OS development. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the key APIs and SDKs for OS development.
1. What are APIs and SDKs?
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): APIs are sets of rules and protocols that allow different software applications to communicate with each other. In OS development, APIs provide standardized methods for interacting with hardware and system resources.
- SDKs (Software Development Kits): SDKs are collections of tools, libraries, and documentation that assist developers in creating software for specific platforms or environments. SDKs often include APIs, compilers, debuggers, and other utilities necessary for development.
2. Key APIs for OS Development

**2.1. Windows API
- Overview: The Windows API (WinAPI) is a set of APIs provided by Microsoft for developing applications and interacting with the Windows operating system.
- Key Features:
- Access to system functions, such as file handling, memory management, and process control.
- Support for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs) with Windows forms and controls.
- Integration with various Windows services and components.
- Best For: Developing applications and system components for Windows operating systems.
**2.2. POSIX API
- Overview: The POSIX (Portable Operating System Interface) API is a standard set of APIs for Unix-like operating systems, including Linux and macOS.
- Key Features:
- Standardized interface for file operations, process management, and threading.
- Provides compatibility and portability across different Unix-based systems.
- Supports multi-threading and inter-process communication.
- Best For: Developing cross-platform applications and system software for Unix-like operating systems.
**2.3. WinRT (Windows Runtime) API
- Overview: The Windows Runtime (WinRT) API is a modern API framework provided by Microsoft for developing Windows Store apps and Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps.
- Key Features:
- Provides a unified API for building applications that run across different Windows devices.
- Supports asynchronous programming and modern UI frameworks.
- Integration with Windows services and components.
- Best For: Developing modern, cross-device applications for the Windows ecosystem.
**2.4. Android NDK (Native Development Kit)
- Overview: The Android NDK is a set of tools and libraries that allows developers to write native code for Android devices.
- Key Features:
- Provides APIs for low-level access to system resources and hardware.
- Supports C and C++ programming for performance-critical applications.
- Integration with the Android SDK for building and deploying Android apps.
- Best For: Developing high-performance and system-level components for Android devices.
**2.5. iOS SDK
- Overview: The iOS SDK is a development kit provided by Apple for building applications for iOS devices, including iPhones and iPads.
- Key Features:
- Includes APIs for accessing system resources, user interfaces, and hardware features.
- Provides tools for developing, testing, and debugging iOS applications.
- Integration with Xcode, Apple’s integrated development environment (IDE).
- Best For: Developing applications for the iOS platform.
3. Essential SDKs for OS Development
**3.1. GNU Toolchain
- Overview: The GNU Toolchain is a collection of development tools for Unix-like systems, including compilers, debuggers, and build systems.
- Key Features:
- Includes GCC (GNU Compiler Collection) for compiling C, C++, and other languages.
- Provides GDB (GNU Debugger) for debugging applications.
- Supports building and linking libraries and executables.
- Best For: Developing and debugging software for Unix-like operating systems.
**3.2. Intel System Studio
- Overview: Intel System Studio is a suite of development tools for optimizing and debugging applications on Intel processors.
- Key Features:
- Provides compilers, debuggers, and performance analysis tools.
- Supports development for a wide range of Intel architectures and platforms.
- Integration with various development environments and build systems.
- Best For: Optimizing and debugging applications for Intel-based systems.
**3.3. Visual Studio
- Overview: Visual Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) from Microsoft that provides a comprehensive set of tools for developing Windows applications and system software.
- Key Features:
- Includes a powerful editor, debugger, and build system.
- Supports multiple programming languages, including C++, C#, and .NET.
- Integration with Azure and other Microsoft services.
- Best For: Developing and managing Windows applications and system components.
**3.4. Xcode
- Overview: Xcode is Apple’s integrated development environment for macOS, used for building applications for macOS, iOS, watchOS, and tvOS.
- Key Features:
- Provides a comprehensive suite of tools for development, testing, and debugging.
- Includes Interface Builder for designing user interfaces.
- Integration with Apple’s development and deployment services.
- Best For: Developing applications for Apple’s operating systems.
4. Best Practices for Using APIs and SDKs
- Understand the Documentation: Thoroughly read and understand the documentation provided with APIs and SDKs to make the most of their features and capabilities.
- Stay Updated: Keep APIs and SDKs up to date to benefit from the latest features, bug fixes, and security updates.
- Test Extensively: Test applications thoroughly to ensure compatibility and performance across different environments and configurations.
- Leverage Community Support: Utilize community forums, online resources, and developer communities for support and best practices related to APIs and SDKs.
Conclusion
APIs and SDKs play a crucial role in operating system development, providing the tools and resources needed to build, manage, and enhance systems and applications. Understanding and utilizing these tools effectively can streamline development, improve performance, and ensure compatibility across different platforms. Whether you’re developing for Windows, Unix-like systems, Android, iOS, or other environments, leveraging the right APIs and SDKs is key to successful OS development.