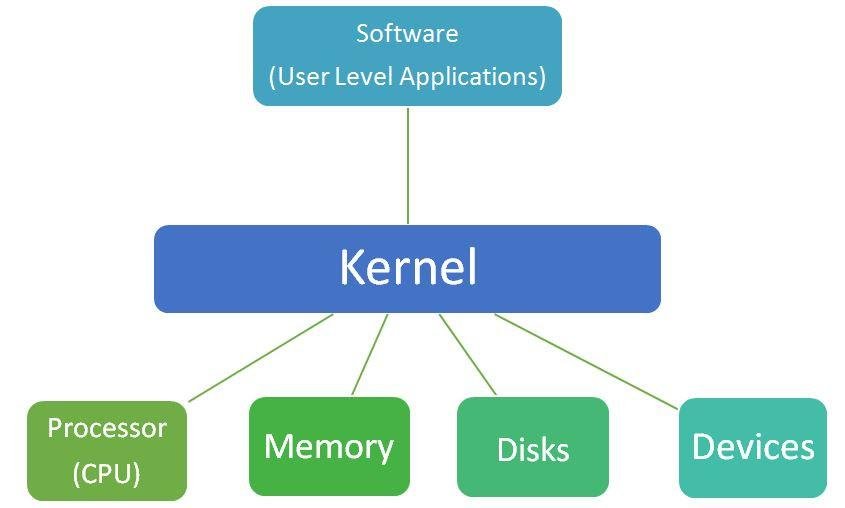
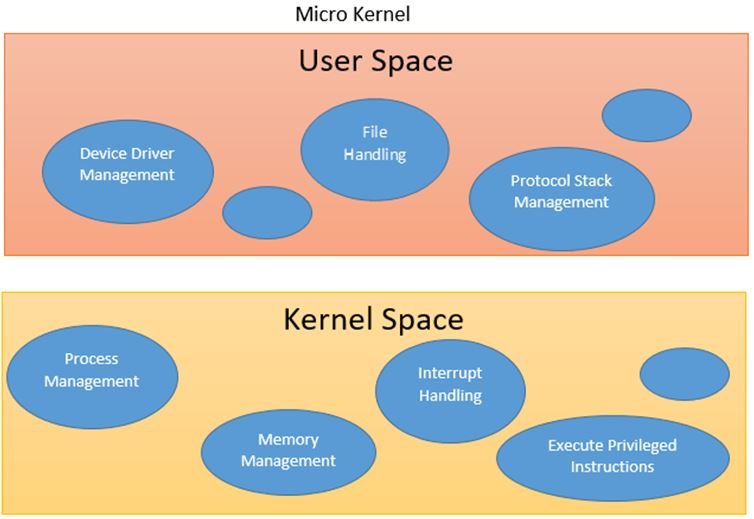
Customizing your operating system can significantly enhance your user experience, allowing you to tailor the environment to your preferences and needs. Whether you use Windows, macOS, or Linux, there are numerous ways to personalize your system. From changing the desktop appearance to modifying system settings, customization can improve productivity and make your OS feel truly your own.

Customizing the Desktop Environment
Start by customizing the desktop environment to suit your style. Change the wallpaper to something that inspires you or use dynamic wallpapers that change throughout the day. Adjust the icon sizes and layout to keep your desktop organized. Many operating systems also allow you to add widgets or gadgets, providing quick access to important information like the weather, calendar, and system performance.
Modifying System Themes
System themes can dramatically alter the look and feel of your OS. Windows and macOS offer built-in themes and dark mode options. For a more personalized touch, you can download custom themes from the internet. Linux users have even more flexibility with themes, as different desktop environments (like GNOME, KDE, and XFCE) offer a variety of customization options. Experiment with different themes until you find one that fits your aesthetic preferences.
Enhancing System Performance
Customizing your operating system isn’t just about looks; it’s also about performance. You can optimize system settings to make your OS run more efficiently. Disable unnecessary startup programs to speed up boot times. Adjust power settings to balance performance and energy consumption. On Windows, you can use the Performance Options menu to fine-tune visual effects. MacOS users can manage system resources through Activity Monitor, while Linux users have tools like htop and systemd-analyze.
Personalizing Keyboard Shortcuts
Custom keyboard shortcuts can streamline your workflow and save time. Most operating systems allow you to create custom shortcuts for frequently used commands and applications. On Windows, use the Shortcut Properties menu to set custom key combinations. MacOS users can configure shortcuts through System Preferences, and Linux users can modify key bindings using desktop environment settings. Customized shortcuts enhance efficiency and make navigation quicker and more intuitive.
Installing Custom Applications and Utilities
Explore custom applications and utilities to enhance your OS functionality. For Windows, tools like Rainmeter can add custom widgets to your desktop, while macOS users might enjoy Bartender for menu bar customization. Linux offers a plethora of open-source applications that can be tailored to fit your needs. Custom applications can add new features, improve system management, and provide better integration with your workflow.
Tweaking System Sounds and Notifications
Personalize your system sounds and notifications to create a more pleasant computing environment. Change the default sounds for actions like startup, shutdown, and error alerts. Customize notification settings to prioritize important alerts and minimize distractions. On Windows, you can adjust sound settings through the Control Panel. MacOS users can make changes in System Preferences, and Linux users can modify sound schemes using desktop environment settings.
Configuring Advanced System Settings
Dive into advanced system settings to unlock more customization options. Windows users can use the Registry Editor to make deeper system changes, while macOS users can access hidden settings through Terminal commands. Linux offers extensive customization through configuration files and command-line tools. Advanced settings allow you to tweak system behavior, manage user permissions, and optimize network settings.
Backup and Restore Custom Settings
After spending time customizing your operating system, ensure you back up your settings. Windows users can use System Restore or third-party tools to create system backups. MacOS users have Time Machine, and Linux users can use rsync or other backup utilities. Regular backups ensure you don’t lose your customizations in case of system failures or updates.
Conclusion
Operating system personalization can transform your computing experience, making it more efficient, aesthetically pleasing, and tailored to your needs. By exploring the various customization options available, you can create an OS environment that boosts productivity and reflects your personal style. Remember to back up your settings to preserve your customizations and enjoy a truly personalized computing experience.